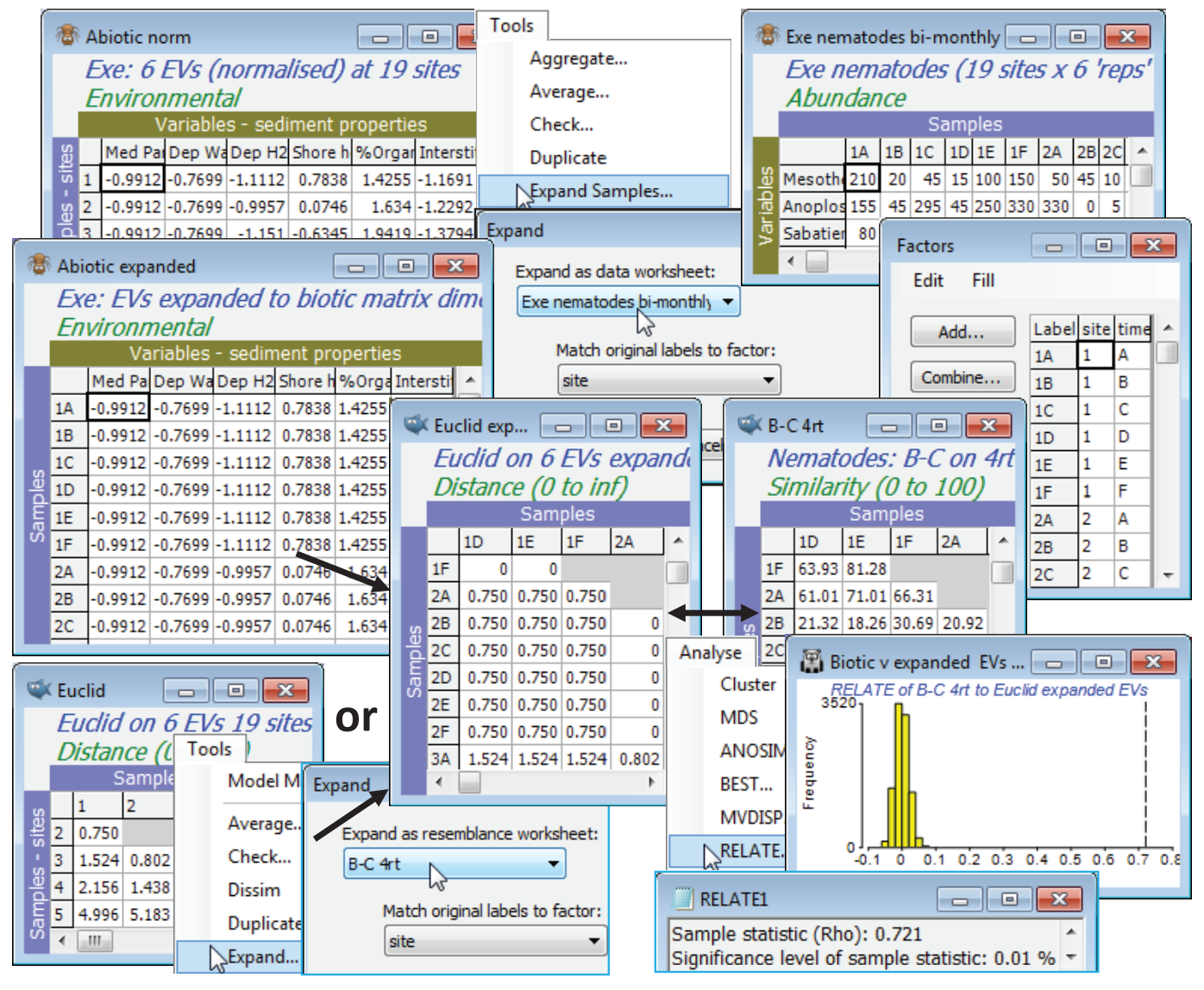
Expand Samples or Expand resemblances
The Exe environment matrix does not seem (from Plots>Draftsman Plot or Histogram Plot) to contain notable outliers and can safely be used without transformation of individual variables. It does however need Pre-treatment>Normalise Variables – rename it Abiotic norm. To expand this data matrix to the dimensions of 108 samples $\times$ 6 variables, with Abiotic norm as the active sheet take Tools>Expand Samples>(Expand as data worksheet: Exe nematodes bi-monthly) & (Match original labels to factor: site). The fourth-root form of the biotic data matrix could equally well have been used in place of the original nematode sheet – what is needed from it is the size of expanded matrix needed, and the structure of samples over the sites, from the factor site whose levels 1, …, 19 are matched up with the labels 1, ..., 19 of the normalised environmental sheet. The expanded environmental matrix is then entered to a Euclidean distance resemblance calculation, to give Euclid expanded. The same construction can be achieved by first taking Euclidean distance on the Abiotic norm data matrix, to give a resemblance matrix renamed Euclid, and then entering this as the active matrix in Tools>Expand>(Expand as resemblance worksheet: B-C 4rt) & (Match original labels to factor: site) to obtain exactly the same model (abiotic) matrix Euclid expanded.
Now with active sheet B-C 4rt a further run of Analyse>RELATE>(Secondary data•Resemblance /model matrix: Euclid expanded) gives a much larger $\rho$ of 0.72 (highly significant, of course, at p<0.01% for the 9999 permutations of this run), indicating the very good fit of the individual bi-monthly samples to the alternative model of sites differences, structured by these abiotic variables.